Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
米谷 佳晃; 丸山 豊*; 平田 文男*; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
Because biomolecules in cell such as proteins, DNA and various small molecules interact with each other in the presence of water molecules, we cannot ignore their hydration when discussing their structural and energetic properties. Although high-resolution crystal structure analyses have given us a view of tightly bound water molecules on their surface, the structural data are still insufficient to capture the detailed configurations of water molecules around the surface of these biomolecules. Thanks to the invention of various computational algorithms, computer simulations can now provide an atomic view of hydration. In this presentation, we describe the hydration patterns of DNA calculated using two distinct computational methods, MD simulation and 3D-RISM theory. The B-form of DNA is suitable for the evaluation of calculated hydrations because a well-defined hydration pattern known as water spine appears in the minor groove of particular sequences. Both methods are promising for obtaining hydration properties, but until now there have been no thorough comparisons of the 3D distributions of hydrating water. Our rigorous comparison showed that MD and 3D-RISM provide essentially similar hydration patterns when there is sufficient sampling time for MD and a sufficient number of conformations to describe molecular flexibility for 3D-RISM. This suggests that these two computational methods can be used to complement one another when evaluating the reliability of the calculated hydration patterns.
 2 chain (IL-13R
2 chain (IL-13R 2)
2)松本 富美子; 玉田 太郎; 本庄 栄二郎*; 太田 昭一郎*; 出原 賢治*; 黒木 良太
no journal, ,
アレルギー性疾患は喘息やアトピー性皮膚炎などに代表される炎症性の疾患で、近年劇的に増加しつつある。インターロイキン13(IL-13)は、T細胞を介した免疫応答を引き起こすタンパク質であり、アレルギー疾患において重要な役割を果たしている。IL-13は2種類の異なった作用を持つ受容体に結合することが知られ、IL-13R 1あるいはIL-13R
1あるいはIL-13R 1/IL-4受容体への結合は細胞内シグナル伝達を促進し、またIL-13R
1/IL-4受容体への結合は細胞内シグナル伝達を促進し、またIL-13R 2への結合は細胞内シグナル伝達を抑制する。IL-13R
2への結合は細胞内シグナル伝達を抑制する。IL-13R 1とIL-13R
1とIL-13R 2の細胞外ドメインはクラス1サイトカイン受容体スーパーファミリー共通の構造と近似したアミノ酸配列を保存しているにもかかわらず、IL-13に対するIL-13R
2の細胞外ドメインはクラス1サイトカイン受容体スーパーファミリー共通の構造と近似したアミノ酸配列を保存しているにもかかわらず、IL-13に対するIL-13R 2の親和性はIL-13R
2の親和性はIL-13R 1のそれと比較して約10倍高い。すなわちIL-13R
1のそれと比較して約10倍高い。すなわちIL-13R 2/IL-13の詳細な構造情報は、強力な抗アレルギー作用を持つ新規有用分子の創生に役立つと考えられる。そこでわれわれは、カイコ-バキュロウイルス発現系を用いてIL-13R
2/IL-13の詳細な構造情報は、強力な抗アレルギー作用を持つ新規有用分子の創生に役立つと考えられる。そこでわれわれは、カイコ-バキュロウイルス発現系を用いてIL-13R 2の細胞外ドメインを発現させることを試みた。IL-13R
2の細胞外ドメインを発現させることを試みた。IL-13R 2は、マウスIgG2aのFcとの融合タンパク質として発現した。発現したIL-13R
2は、マウスIgG2aのFcとの融合タンパク質として発現した。発現したIL-13R 2-Fcは、プロテインGカラムにより精製したのち、イオン交換,ゲル濾過カラムにより高純度に精製することができた。IL-13とIL-13R
2-Fcは、プロテインGカラムにより精製したのち、イオン交換,ゲル濾過カラムにより高純度に精製することができた。IL-13とIL-13R 2-Fcとの親和性はゲル濾過-光散乱装置により解析し、IL-13とIL-13R
2-Fcとの親和性はゲル濾過-光散乱装置により解析し、IL-13とIL-13R 2-Fcは1:1で強く結合することを明らかにした。
2-Fcは1:1で強く結合することを明らかにした。
中川 洋; 城地 保昌*; 北尾 彰朗*; 片岡 幹雄
no journal, ,
タンパク質ダイナミクスに対する水和効果を理解するために、脱水和状態,中間量の水和状態,水和状態のスタフィロコッカルヌクレアーゼを用いて中性子非弾性散乱実験を行った。極低温において、高エネルギー振動である局所的な運動は水和に依存しなかったのに対し、水和は5meVより低エネルギーの協調的な運動に影響を与えた。顕著な変化はボソンピークの高エネルギーシフトとして観測され、このことはエネルギーランドスケープのローカルミニマムでの調和ポテンシャルがハードニングを起こすことを示している。240Kの動力学転移は水和タンパク質でのみ観測された。300Kで観られる顕著な準弾性散乱は水和タンパク質のみで観測され、これは転移の起源が水和水によって活性化される運動であることを示している。中間量の水和状態のタンパク質の中性子散乱スペクトルは、100Kと200Kでは水和状態とほとんど同じであるが、300Kでは乾燥状態に近い。このことは中間量の水和は調和運動に十分に影響を与えるが、非調和運動に影響を与えるにはある閾値以上の水和量が必要であることを示す。水和は、調和運動と非調和運動の両者に影響を与えるが、その仕組みは異なっている。
石田 恒
no journal, ,
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) maintains genome stability by repairing mismatches that arise through DNA replication errors and during recombination. Defects in MMR result in a significant increase in the spontaneous mutation rate and predispose humans to cancer. In E. coli, the proteins MutS, MutL and MutH are responsible for the MMR. MMR is initiated by MutS, which functions in the homodimer form. MutS recognizes and efficiently binds to mispaired bases and unpaired bases in DNA duplexes. It is thought that the ATPase activity of MutS plays a role in proofreading to verify mismatch binding and authorize the following downstream excision in which MutL and MutS are involved. In order to investigate how the binding of MutS to the DNA and ATP hydrolysis are coordinated, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the wild-type and mutant MutS in water with mismatched and undamaged DNA were performed. Including the water molecules, each system comprised about 200,000 atoms. The MD simulations were carried out at a constant pressure of one bar and a temperature of 300 K for several tens of nanoseconds in total. The binding free energies were calculated using the MM-GBSA method, and the results are consistent with the experimental data. Moreover, the dynamic relationship between the DNA biding and ATPase domain sites was analyzed.
金枝 直子; 石田 恒; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
ヌクレオソームは、クロマチンの基本的な繰り返し構造である。近年、クロマチン・リモデラーがヌクレオソームDNAを、ヒストンタンパク質から引きはがして、DNAのポジショニングを変えているということがわかってきている。この結果としてヌクレオソームにその結合を阻害されていた、転写や複写・制御にかかわるDNA結合たんぱくがヌクレオソームDNAへ結合できるようになっている。この段階における自由エネルギー・プロファイルを明らかにすることは、転写や複写・制御のメカニズムを解明するために、重要な手掛かりを提供するだろう。われわれはまず、高解像度のヌクレオソームの結晶構造を水とイオンを含めて、MDシミュレーションする。平衡化の後、ヌクレオソームDNAの端をひっぱり、ヒストンたんぱくから引きはがし、その過程における自由エネルギー・プロファイルを描く。さらにヒストン修飾の影響も調べる。
小野 正人; 村上 洋; 一ノ瀬 暢之*
no journal, ,
逆ミセル内の分子ダイナミクスの解明は、逆ミセルを用いた反応制御などの応用的観点だけでなく、分子ダイナミクスのナノメートル空間拘束効果などの学術的観点からも重要である。本研究の目的は、色素分子を含んだ水逆ミセル及び人工色素蛋白質逆ミセルの逆ミセルサイズに依存した分子ダイナミクスを調べることである。逆ミセルでは、実験的にそのサイズを変えることができ、分子周辺の環境を変えた実験が可能である。溶液中で電子励起した色素分子の蛍光スペクトルは、分子周辺の配置変化に起因した緩和過程により、時間とともに低エネルギー側にシフトしていくため、その時間シフトを観測することにより蛍光分子周辺のダイナミクスを研究することができる。結果として、両試料に対して、逆ミセルサイズの増加に伴い緩和速度が速くなり、色素分子に作用している水分子の数が多いほど緩和速度が速くなると考えられる。また、逆ミセル内の水分子の層数が両試料において同じとき、水逆ミセルよりも人工色素蛋白質逆ミセルの緩和速度が速く、蛋白質が水和されることで柔軟な運動が可能となったことを示唆している。
徳久 淳師; 高 潤一郎; 河野 秀俊; 郷 信広*
no journal, ,
New light sources of X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) are under construction in Europe, USA and Japan. XFEL offers a new possibility in imaging single biological macromolecules. Our goal is to develop a computational method for the determination of molecule 3D structures from diffraction intensity data by XFEL. A straight forward procedure would be (1) to classify and average 2D diffraction patterns to improve the S/N ratio, (2) to obtain a 3D diffraction pattern by determining the relative positions of averaged-2D-images and (3) to retrieve the phases and construct the 3D structure using the over-sampling method. One of the big problems is the quantum noise resulting from the extremely weak intensity of elastically diffracted X-ray. Algorithms for structure determination must be developed to process the experimental data immersed in the quantum noise. In this meeting we report detailed procedures of analysis of experimental diffraction intensity data to be obtained 3D structure.
藤原 悟; 松本 富美子; 中川 洋; 遠藤 仁*; 小田 俊郎*
no journal, ,
F-アクチンの細胞運動や輸送等にかかわる実に多様な機能を可能とするF-アクチンの柔らかさの起源を解明し、機能多様性の分子機構を明らかにするための第一段階として、さまざまな時空間階層における運動モードのうち、ピコ ナノ秒領域におけるアクチンのダイナミクスの測定を行った。東京大学物性研究所所有の中性子スピンエコー分光器(iNSE)を用いて、時間領域30ナノ秒までのQ-領域0.03
ナノ秒領域におけるアクチンのダイナミクスの測定を行った。東京大学物性研究所所有の中性子スピンエコー分光器(iNSE)を用いて、時間領域30ナノ秒までのQ-領域0.03 0.2
0.2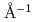 の中性子スピンエコー測定を、F-アクチン溶液及びその対照としての単量体G-アクチン溶液のそれぞれについて行った。この時空間領域は、蛋白質の並進拡散や蛋白質内ドメインの運動などの起こる領域に対応し、中性子スピンエコー法によってのみ測定可能な時空領域である。得られた中間関数から、F-アクチン及びG-アクチンのいずれも単一の緩和過程で記述できることが示された。そして、緩和の早さ、すなわち(みかけの)拡散係数がF-アクチンの方が小さくなることが明らかとなった。G-アクチン及びF-アクチンのいずれも、単純な溶液中の自由併進拡散のみでなく、内部運動が影響していることが示唆された。
の中性子スピンエコー測定を、F-アクチン溶液及びその対照としての単量体G-アクチン溶液のそれぞれについて行った。この時空間領域は、蛋白質の並進拡散や蛋白質内ドメインの運動などの起こる領域に対応し、中性子スピンエコー法によってのみ測定可能な時空領域である。得られた中間関数から、F-アクチン及びG-アクチンのいずれも単一の緩和過程で記述できることが示された。そして、緩和の早さ、すなわち(みかけの)拡散係数がF-アクチンの方が小さくなることが明らかとなった。G-アクチン及びF-アクチンのいずれも、単純な溶液中の自由併進拡散のみでなく、内部運動が影響していることが示唆された。
玉田 太郎; 木下 誉富*; 栗原 和男; 安達 基泰; 大原 高志; 多田 俊治*; 黒木 良太
no journal, ,
セリンプロテアーゼの触媒機構を理解することを目的として、ブタ膵臓エラスターゼの高分解能中性子及びX線構造解析を正四面体型中間体を模倣する阻害剤と複合体の状態で実施した。同一の大型単結晶を用いた室温における測定の結果、1.65 分解能の中性子回折データ及び1.20
分解能の中性子回折データ及び1.20 分解能のX線回折データを取得した。また、別の結晶を用いて100K下で0.94
分解能のX線回折データを取得した。また、別の結晶を用いて100K下で0.94 分解能のX線回折データも併せて取得した。今回の解析は、セリンプロテアーゼとしてはこれまでで最も高分解能で実施された中性子構造解析例である。中性子とX線の両解析結果からHis57とAsp102の間に形成された水素結合は結合距離が2.60
分解能のX線回折データも併せて取得した。今回の解析は、セリンプロテアーゼとしてはこれまでで最も高分解能で実施された中性子構造解析例である。中性子とX線の両解析結果からHis57とAsp102の間に形成された水素結合は結合距離が2.60 と短く、強い水素結合であると判明したものの、水素原子はHis57に結合してしていた。この結果は、一説として唱えられている低障壁水素結合の特徴(水素原子がドナーとアクセプターの中間付近に存在する)は満たすものではなく、低障壁水素結合仮説を否定するものであった。また、中性子解析結果から、いわゆるオキシアニオンホールの形成とオキシアニオンホール中に阻害剤由来の酸素原子が酸素陰イオンの状態で存在していることが明瞭に示された。これより、セリンプロテアーゼの触媒機構において正四面体型中間体構造の安定化に対するオキシアニオンホールの役割が明らかになった。
と短く、強い水素結合であると判明したものの、水素原子はHis57に結合してしていた。この結果は、一説として唱えられている低障壁水素結合の特徴(水素原子がドナーとアクセプターの中間付近に存在する)は満たすものではなく、低障壁水素結合仮説を否定するものであった。また、中性子解析結果から、いわゆるオキシアニオンホールの形成とオキシアニオンホール中に阻害剤由来の酸素原子が酸素陰イオンの状態で存在していることが明瞭に示された。これより、セリンプロテアーゼの触媒機構において正四面体型中間体構造の安定化に対するオキシアニオンホールの役割が明らかになった。
樋口 真理子; Pinak, M.; 斎藤 公明
no journal, ,
放射線により、10から20ベースペア以内に複数の損傷が生じることがあり、これをクラスター損傷と呼ぶ。クラスター損傷は単独損傷と比較して修復が阻害される傾向がある。8オキソグアニンの相補鎖上の数ベースペア離れた位置に一本鎖鎖切断がある損傷は修復が困難なクラスター損傷の例である。このクラスター損傷は修復酵素hOGG1による8オキソグアニンの修復を阻害することが実験によりわかっている。しかし、クラスター損傷の修復阻害の分子的な機構は解明されていない。本研究では損傷DNAと修復酵素hOGG1の分子動力学シミュレーションを用いて修復阻害の解明を目指した。8オキソグアニン単独損傷の場合と、8オキソグアニンと一本鎖鎖切断のクラスター損傷の場合を比較した。その結果、単独損傷の場合は修復のための酵素反応が生じる部位に8オキソグアニンが近づいた構造が安定であったのに対し、鎖切断がある場合は酵素反応を生じる部位以外でも8オキソグアニンが安定に存在してしまう、すなわち、修復が起きる確率が低くなることがわかった。
藤井 聡*; 河野 秀俊; 郷 信広*; 皿井 明倫*
no journal, ,
Sequence-dependent conformational properties of DNA play important roles in various biological processes. For example, interactions of proteins with DNA sequences are known to be affected by the conformational properties of DNA. Proteins such as TATA-box binding protein and catalytic protein DNaseI induce the DNA conformation to bent form and A-form at recognition sites, respectively. It has been known that these conformational transitions are induced by the environment: variations in ionic strength and identity, sequence, water activity, and ligand/protein binding all can modulate DNA structure. In this study, we analyzed how the sequence and water activity influence the DNA conformations using molecular dynamics simulations.
山崎 智*; 福井 一彦*; 河野 秀俊; 清水 謙多郎*; 皿井 明倫*; 寺田 透*
no journal, ,
Sequence-specific recognition of DNA by proteins plays a critical role in regulating gene expression. Accurate recognition is achieved by a combination of two different mechanisms. The first is direct readout, in which recognition is mediated by direct interactions between the protein and the DNA bases. The second is indirect readout, which is caused by the sequence-dependence of the conformation and deformability of the DNA structure. In our previous study, the contributions of indirect readout to binding affinity were evaluated for every tetrameric step in given protein-DNA complex structures. Using sequence-structure threading, potential energy differences between native and non-native tetrameric sequences for given tetrameric step conformation were compared. These potential energy functions were derived from the probability distribution function of its tetrameric step conformations calculated from trajectories of MD simulations of free DNAs which include all 136 types of tetramers. This gave good agreement with some experimental results, but shortage of structural sampling made the accurate estimation of distribution function difficult. In this work, we estimate the probability of occurrence of each tetrameric step sequence on given tetrameric step conformation using a Bayesian approach using the same structural dataset. We apply this approach to known protein-DNA complex structures, and assess the performance of predicting the sequence region where indirect readout makes important contribution to the binding affinity.
田中 昭宏*; 藤井 聡*; 河野 秀俊; 皿井 明倫*
no journal, ,
Gene regulation is achieved by a complex combination of transcription factors and their targets. This is highly cooperative nonlinear system, in which minute changes in input signal are amplified to produce highly visible outcome. Thus, it is crucial to understand the role of cooperativity in gene regulation. Here, we focus on the structural aspect of cooperativity at the protein-DNA recognition level. We have used a knowledge-based approach, utilizing structural data of protein-DNA complexes, to derive empirical potential for the specific interactions between bases and amino acids. Then, these potentials were used to quantify the specificity of protein-DNA recognition. In this study, we apply this method to examine the effects of binding cooperativity on the specificity of protein-DNA recognition. For this purpose, we collected structures of protein-DNA complexes, with a protein bound to DNA and the same protein together with its partner bound to DNA. By computing the specificity for these homo- and hetero-complexes, we can examine if the cooperative binding enhance the specificity in a systematic manner. We also examined the conformation changes of proteins and DNAs between the homo- and hetero-complexes, to find any relationship between structure and specificity in the cooperative recognition. We show by several examples that the protein-DNA recognition is indeed cooperative and the specificity is enhanced by structural changes during the recognition.
 and an attempt to locally targeted microbeam irradiation
and an attempt to locally targeted microbeam irradiation坂下 哲哉
no journal, ,
神経系のモデル生物として知られる線虫を用いて、化学走性学習に対する放射線( 線)照射の影響を調べた。その結果、化学走性学習の能力は、比較的高線量(500Gy)の放射線を照射しても有意な影響を受けないが、学習過程の途中に放射線を照射した場合にだけ、照射直後の化学走性が有意に低下することを発見した。また、この放射線照射に対する応答が、
線)照射の影響を調べた。その結果、化学走性学習の能力は、比較的高線量(500Gy)の放射線を照射しても有意な影響を受けないが、学習過程の途中に放射線を照射した場合にだけ、照射直後の化学走性が有意に低下することを発見した。また、この放射線照射に対する応答が、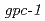 変異体において有意に抑制されることを見いだした。これらの結果は、線虫の化学走性学習に対する放射線照射の影響が、特定の感覚神経に局在するGPC-1タンパク質を介して修飾的に働く可能性を示唆する。さらに、現在、原子力機構の重イオンマイクロビーム照射装置を用いて、線虫の神経細胞を照射する研究を進めている。研究の現状と今後について概説する。
変異体において有意に抑制されることを見いだした。これらの結果は、線虫の化学走性学習に対する放射線照射の影響が、特定の感覚神経に局在するGPC-1タンパク質を介して修飾的に働く可能性を示唆する。さらに、現在、原子力機構の重イオンマイクロビーム照射装置を用いて、線虫の神経細胞を照射する研究を進めている。研究の現状と今後について概説する。